In-depth analysis of the impact of environmental regulations on the wheel balance weight market
The evolution of global environmental regulations
The wheel balance weight industry has undergone significant environmental regulatory changes in the past 20 years, which can be divided into several key stages:
1. Early stage (before 2000):
- Lead wheel weights occupy more than 95% of the market share;
- No clear environmental restrictions;
- Production costs dominate market choices;
2. Transition period (2000-2010):
- The EU RoHS Directive (2003) first restricted the use of lead in electronic devices;
- The US EPA began to pay attention to lead pollution;
- Zinc wheel weights entered the market as a substitute;
3. Transformation period (2011-2020):
- The EU ELV Directive clearly restricted the use of lead in vehicles;
- California took the lead in banning the sale of lead wheel weights in the United States;
- Major automakers began to require suppliers to provide lead-free solutions;
4. Current stage (2021 to present):
- The major global markets have basically completed the transition to lead-free balance weights;
- Environmental standards extend to full life cycle assessment;
- Carbon footprint becomes a new consideration;
Comparative analysis of major market regulations
| Regulation | Regulation | Effective Date | Core Requirements | Permitted Materials | Penalties |
| EU | ELV Directive | 2003/2013 (revised) | Bans lead in auto parts | Zinc, steel, composites | Recalls + fines |
| U.S. | EPA Lead Restrictions | State-by-state | 15 states ban lead weights | Primarily zinc | Sales bans |
| China | GB Standards | 2018 (updated) | Encourages lead-free transition | Lead still allowed in transition | Tax adjustments |
| Japan | JIS D4205 | 2015 | Automaker supply chain requirements | Zinc/steel | Market restrictions |
| India | None yet | - | Voluntary standards | Lead still dominant | - |
The overall impact of environmental regulations on the industry chain
1. Upstream material market restructuring
- Zinc price fluctuations: Global zinc demand increased by 30% (2010-2020)
- New material research and development: R&D investment in composite materials increased by 15% annually
- Supply chain certification: ISO 14001 becomes the basic threshold
2. Midstream manufacturing transformation
- Equipment transformation: Lead casting → zinc stamping production line conversion cost is about $500,000/production line
- Process adjustment:
Zinc blocks require higher stamping accuracy (±0.1g → ±0.05g)
The temperature resistance requirements of viscous balance block glue are increased (-40℃~120℃) - Cost structure changes:
Lead block cost: $0.02-0.05/g
Zinc block cost: $0.08-0.12/g
Composite materials: $0.15-0.30/g
3. Downstream application market differentiation
- OEM market: 100% lead-free (standard of major automakers)
- Aftermarket:
Developed countries: 80% lead-free penetration
Developing countries: 30-50% lead products still exist - Special applications:
Racing field accepts high-cost new materials
Military vehicles retain some lead exceptions
Corporate Compliance Strategy Case Analysis
Case 1: Transformation path of a leading European supplier
- Invested 20 million euros in 2008 to build a zinc stamping line
- Developed a recyclable viscous balance block system in 2012
- Obtained "zero lead supply chain" certification from automakers in 2016
- Carbon footprint 40% lower than the industry average in 2020
Case 2: Lessons from traditional North American manufacturers
- Delayed response to California ban led to loss of 15% market share
- Emergency transformation incurred an additional $3 million in costs
- After the brand image was damaged, it took 5 years to rebuild
Case 3: Overtaking on the curve of Asian emerging companies
- Directly positioned in the high-end lead-free market
- Innovative use of recycled zinc materialsBecame a core supplier of Japanese automakers within 3 years
Prediction of future regulatory trends
1. Extended producer responsibility (EPR):
- Balance block recycling rate requirements (EU expected to set 70% target in 2025)
- Mandatory proportion of recycled content
2. Impact of Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM):
- High carbon footprint products face additional tariffs
- Demand for cleaner zinc smelting processes
3. Full material disclosure requirements:
- Possible restrictions on specific chemical components in current adhesives
- Material traceability becomes a basic requirement
4. Regional standard differences:
- Developed countries move towards "zero heavy metals"
- Emerging markets may skip the lead stage and directly adopt new materials
Industry response suggestions
1. Product strategy adjustment
Material combination optimization:
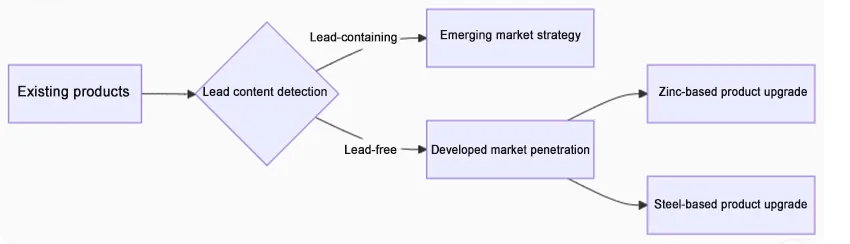
Certification system construction:
- Must obtain: IMDS, RoHS, REACH
- Recommended: Cradle to Cradle, EPD
2. Transformation of production operations
Process innovation direction:
- Precision improvement technology for zinc stamping
- Application of low-VOC adhesives
- Closed-loop recycling system for waste materials
Cost control measures:
- Zinc material centralized procurement alliance
- Mold life extension plan
- Lean production implementation
3. Market strategy optimization
Regional differentiated supply:
- Developed countries: Emphasis on environmental certification
- Emerging markets: Highlight cost-effective transition plan
Customer education plan:
- Technical training for repair shops
- Popular science content for end consumers
- Participate in the formulation of industry standards
4. R&D key recommendations
- Zinc alloy formula optimization (hardness/density balance)
- Development of bio-based adhesives
- Adjustable smart balance block concept
- Design for easy recycling and disassembly
Environmental regulations have fundamentally reshaped the competitive landscape of the wheel wegiht industry and will continue to drive technological innovation and market restructuring. Companies need to establish a regulatory early warning mechanism to transform environmental compliance into a competitive advantage rather than simply viewing it as a cost burden. In the next five years, the industry will witness the deep integration of material science, circular economy and digital services to create new value growth points.
